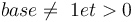Logarithmes : Différence entre versions
De TravauxIndse
| Ligne 11 : | Ligne 11 : | ||
* <math> log_a (y) = x \Leftrightarrow y = a^{x} </math> | * <math> log_a (y) = x \Leftrightarrow y = a^{x} </math> | ||
* <math> log_{10} \left ( x \right ) = log (x) </math> | * <math> log_{10} \left ( x \right ) = log (x) </math> | ||
| − | * <math> log_{e} \left ( x \right ) = ln (x) </math> (logarithme népérien [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yNMm791keMU]) | + | * <math> log_{e} \left ( x \right ) = ln (x) </math> (logarithme népérien [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yNMm791keMU])<math> \rightarrow \</math> [http://xmaths.free.fr/TS/cours/cours.php?nomcours=TSlncours&page=01|Exercices (+petite explication théorique)] |
* <math> log_a \left ( u.v \right ) = log_a u + log_a v </math> | * <math> log_a \left ( u.v \right ) = log_a u + log_a v </math> | ||
* <math> log_a \left ( \frac{u}{v} \right ) = log_a u - log_a v </math> | * <math> log_a \left ( \frac{u}{v} \right ) = log_a u - log_a v </math> | ||
Version du 20 février 2014 à 09:50
Wikipédia : [1]
Les fonctions logarithmiques sont les réciproques des fonctions exponentielles car elles sont bijectives (C'est-à-dire que tout élément de l'ensemble d'arrivée a un et un seul antécédent [2] ).
Si 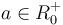 alors le logarithme en base a d'un réel strictement positif est l'exposant de la puissance de a égale à ce réel.
alors le logarithme en base a d'un réel strictement positif est l'exposant de la puissance de a égale à ce réel.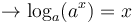
Quelques propriétés et définitions à retenir :
-
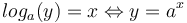
-
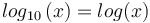
-
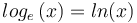 (logarithme népérien [3])Échec d'analyse (L’exécutable <code>texvc</code> est introuvable. Lisez math/README pour le configurer.): \rightarrow \
(+petite explication théorique)
(logarithme népérien [3])Échec d'analyse (L’exécutable <code>texvc</code> est introuvable. Lisez math/README pour le configurer.): \rightarrow \
(+petite explication théorique) -
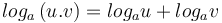
-
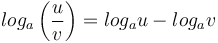
-
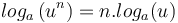
- Changement de base [4] :
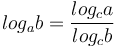
Attention ! Ne pas oublier le domaine de définitions !!
Conditions d'existences :